As we all know, anything that runs on electricity generates an amount of heat to some degree, whether it's your television, mobile phone or desktop PC. And in the case of a modern computer, several parts inside can get incredibly hot, even up to the boiling point of water! Generally speaking, the hotter an electrical component operates, the shorter its lifespan could potentially be because of the extra stress it has to endure.
Dec 28, 2015 Motherboard temperature monitoring with Monit allows you to keep a check on your server for adequate cooling. Monit is an automatic monitoring, maintenance, and repair utility for Unix systems. If the motherboard temperature is high Monit will send you an email alert. You can then examine and resolve any issues. The temperature readings are accurate when compared to an infrared point temperature reader, the motherboard BIOS and Windows software. The length is perfect @ 50c. It reaches across the motherboard to the heat pipe on the GPU and the PSU or other devices. The shielding is nice.
Computers have always had devices inside them such as heat sinks and fans to try and cool the hardware components down as much as possible and stop any problems related to excessive heat occurring. Sometimes though the processor, graphics card, power supply or even a hard drive might be getting hotter than needed because of inefficient cooling, dust build up or simply a faulty fan somewhere. The CPU could run into problems such as shutting down the system unexpectedly if it gets too hot.
Are you worried your computer might be running a little hotter than it should be, an overclocker trying to push the system to its limit, or just somebody who is curious to know how hot a certain hardware component is getting or if the cooling fans are running properly?
Most components inside a modern PC include some form of monitoring sensors that can tell you things like temperatures, power draw, fan speeds etc. One of the ways to find these values on most systems is in the BIOS. But obviously you're not going to sit in there all day just to look at those values! An easier way is to use a Windows utility to get the information for you and then you can monitor things from the relative comfort of your desktop.Here's a selection of tools that can monitor your system hardware and give you information you might find helpful such as your CPU temperature, or cooler fan speeds, or even the output values of the power supply. Do note that this list is for hardware monitoring tools only, if you want a combined hardware information and monitoring program such as Speccy or HWInfo, then look at our other article which includes these tools.
1. HWMonitor
Made by CPUID who are also responsible for CPU-Z and PC Wizard, HWMonitor is a great tool for displaying the majority of your systems temperatures, fan speeds and voltages. There are no real options as such, apart from a function to save monitoring or SMBus data to a text file. Download to dropbox chrome. 3 sets of values are displayed; the current values and the minimum / maximum values since the program was started.
What most people like about HWMonitor is the clear and easy to read layout of all the values in one window for you to quickly scan for what readings you're looking for. It doesn't do anything else like controlling fan speeds or setting warning alarms, but for a simple display of all the relevant values, HWMonitor is hard to beat. There is a setup installer or separate 32-bit / 64-bit portable versions available.
Download HWMonitor
2. Speedfan
Speedfan has been around a long time and is widely considered to be one of the best tools around to monitor just about every temperature, fan speed and voltage your system can provide and also control the speed of the fans if they run too slow or too fast and therefore noisy. Warnings can be set for the temperatures, there is S.M.A.R.T. information for the hard drives, and just about any value the program displays can be logged to a file. You can even set a trigger event of running a program or sending an email etc if a temperature reaches a certain value.
A graph is also available for any of the Temperature, fan speed or voltage readings you want to include. Speedfan does require a bit of setting up to get things configured to your liking, but there aren't many other tools around with such control of fan speeds, alarms, logging etc. Sadly there is no portable version, but the installer contains no adware of any kind, so is well worth installing.
Download Speedfan
3. Open Hardware Monitor
We said previously that HWMonitor was hard to beat at displaying all the needed values in an easy to read window, well Open Hardware Monitor is probably the one tool that beats it and has been our clear favorite monitoring tool for a few years. In addition to temperatures, fan speeds and voltages, this tool can also display detailed CPU / GPU frequencies and load, memory information, hard drive storage space and remaining life and data throughput of SSD's.
Add to that an optional plot graph for all available temperature sensors, and a desktop gadget that can display any value from the main window by right clicking on it and selecting 'Show in gadget', and you can see why Open Hardware Monitor is such a great program. Each value can also be renamed or hidden and some readings have a Parameter option to to adjust things like the offset etc. Open Hardware Monitor is a portable program and to get all the available readings make sure to run the program as Administrator.
Download Open Hardware Monitor
4. Core Temp
As the name suggest, Core Temp focuses mainly on providing accurate information for the core temperature values which are those from inside the CPU itself as opposed to the metal casing. There is also offset correction options and a Overheat Protection option which can set up notifications or sleep / hibernate / shutdown the machine when a certain temperature is reached. Owners of the Logitech G15 keybaord have an option to enable Core Temp readings on their LCD display.
The program doesn't support older processors like Pentium 4 or Athlon XP, but does have an interesting plugin feature where you can add in things like a sidebar gadget, graphs and also the option to get real time temperatures sent direct to your Android smartphone. Be careful if using the installer version as it contains InstallQ adware, or simply use the 32-bit / 64-bit portable version by clicking on 'More Downloads'.
Download Core Temp
5. Real Temp
Real Temp is similar to Core Temp in that it concentrates mainly on the core temperatures inside your Intel processor, not AMD. This is a different reading from the other single CPU temperature value found inside your BIOS. The 'Distance to TJ Max' value could throttle or shut down the machine if it reaches zero, but the TJ Max value itself is actually unknown for most desktop processors, and therefore the options to edit this value are best left to experienced users.
A small benchmark can be performed using the XS Bench button and there are alarms that can be set for CPU and GPU temperatures. A reading for AMD or Nvidia cards can be turned on from the settings window as can temperatures in the system tray area. Real Temp is a portable only program.
Download Real Temp
6. Hardware Sensors Monitor
This program isn't free and the full version is a rather pricey $34 if you want the extras of HDD S.M.A.R.T. and GPU monitoring or CPU throttling. The demo also only runs for 10 minutes at a time and has a 14 day limit, but Hardware Sensors Monitor can still be useful to quickly check the motherboard, hard drive, graphics card and CPU temperatures as well as fans speeds and voltages, complete with a couple of small graphs if you click on the arrow next to the section title.
There are options in the settings window to make corrections to the temperatures, and several alarms can also be configured, but probably isn't worth troubling yourself with in the free versions 10 minute time limit. Only an installer version is available.
Download Hardware Sensors Monitor
7. OCCT
OCCT is not actually primarily a hardware monitoring program, but a system stress tester which is useful to run and see what temperatures your system reaches under maximum load. There is however, no need need to use that part of the program if you don't want because one of the 2 main windows is a standard hardware monitor complete with graphs to display sensor information such as power / CPU voltages, both sets of CPU temperatures, various frequencies and also memory and CPU usage.
There are 3 different displays; graph, text or a mixture of both and extra values could be available in the settings which can be enabled or disabled. OCCT uses a built in version of HWMonitor to provide its values which can be changed to other 3rd party tools such as Aida64 or Core Temp. Portable or installer versions are available, but you can't get rid of the awful color scheme!
Download OCCT
You might also like:
Find Your Maximum CPU Temperature11 Tools to Find out Information About Your Computer's Hardware2 Tools to Monitor Specific Processes and Trigger actions10 Stress Test Tools to Determine the Stability of Your Computer5 Free Tools To Monitor And Log Your Internet TrafficMotherboard Temperature Monitor Software
Are there any power supplies with heat sensors? I'm curious how fast that power supply fan needs to run. At 5 volts its totally inaudible. The direct mail company list. But what if its stressed?
ReplySome of the Corsair PSUs have monitoring for all sorts of things, I have an AX860i and can see fan speed, temperature, load, efficiency, etc.
ReplyCPUiD HWWizard used to be the best tool by far in my opinion then they dumped it for some reason and now their charging users to support the bs their puttin out here
ReplyHWinfo does indeed trump all these.
ReplyAlso – MSI Afterburner good for graphs of GPU temps and stats for tuning
msi.com/page/afterburner
ReplyGood overview – Intel's Exteme Tuning Utility very good too, with graphs etc – downloadcenter.intel.com/download/24075/Intel-Extreme-Tuning-Utility-Intel-XTU-
ReplyI want to install a program such as these, but I'm a bit confused about which of these might be 'Gadgets' as opposed to programs or apps. I had 'Gadgets' installed on my Windows 7 machine with all of this information and loved them, but was warned repeatedly not to install them again on my Windows 10 machine as they are unsafe.
I want an always on floating on the desktop solution.
ReplyAs the screenshots show, these are all tools that have their own window on the desktop.
Something like Open Hardware Monitor has the option of a gadget which you can manually switch on.
ReplyHWinfo kicks their ass.
Replyyour blog kicks ass, raymond!
really!
~rob :)

Nice tool Raymond!
ReplyLeave a Reply
(*This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may receive a small commission if you choose to purchase through links I provide (at no extra cost to you). Thank you for supporting the work I put into this site!)
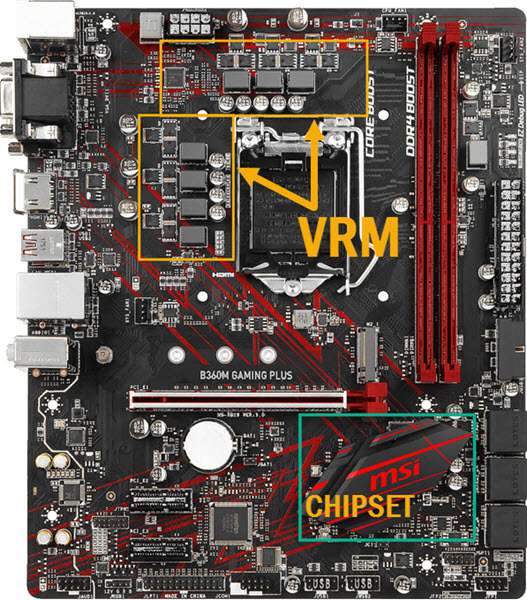
If your motherboard chipset and VRM gets very hot, then they can lead to instability and other issues with your PC. VRM or Voltage Regulator Module is responsible for providing power to your processor or CPU and RAM. It converts higher 12V or 5V voltages from the PSU to a much lower voltage (1.2V or so) that is required by the CPU or processor. VRM mainly consists of MOSFETs, Inductors or Chokes, Capacitors, and a Logic Unit which is an Integrated Circuit (IC) and is called the PWM controller. MOSFETs are the main element of a VRM, and they can get very hot during high CPU usage, and especially during overclocking. Almost all of the mid-range and high-end motherboards come with heatsinks over VRMs for overclocking, so as to prevent them from overheating and thus avoiding any kind of system instability and unexpected shutdown.
Modern-day motherboard chipsets consist of I/O channels and Interfaces that include SATA ports, USB ports, RAID support, some PCI-E lanes and maybe some other things depending on the chipset. Basically, a motherboard chipset allows I/O devices and components to communicate with the CPU. Intel calls their motherboard chipset as PCH (Platform Hub Controller), whereas AMD calls it FCH (Fusion Controller Hub) or just motherboard chipset only.
A low-end motherboard chipset may not get that hot, but a mid-range and high-end motherboard chipset can get very hot and they are generally equipped with bigger heatsinks. Motherboard chipsets generally remain within the safe temperature range, but if they cross the threshold temperature then you can face various issues regarding stability.
Monitoring and knowing about your VRM and Motherboard temperature is very important, when you are facing any kind of instability issues with your system because these components often get ignored most of the time. So, here I am going to list down various methods to find out your motherboard chipset and VRM temperature, so that can you can take appropriate measures to cool them down.
How to Check VRM & Chipset Temperature
Here are the various methods and techniques by which you can monitor your motherboard's chipset and VRM temperature. Most of these methods can also be used to measure graphics card VRM temperature, and the temperature of its, GPU & VRAM.
HWiNFO
The easiest way to find out VRM and chipset temperature is by using HWiNFO, which is a very good hardware information and monitoring tool or utility. It should be noted that this method only works if your motherboard has built-in sensors for VRM and Chipset temperature monitoring. To know about the temperature of your motherboard chipset and VRM, launch the HWiNFO program, and from Menu bar, go to Monitoring->Sensor status. A window will open, and here scroll down to your motherboard section. For example, the motherboard listed here is Gigabyte B250-D2V-CF. Below that, you will find temperature readings for System, PCH, CPU and VRM MOS. PCH is your motherboard chipset and VRM MOS is the temperature of the MOSFETs of VRM, which are the main components of VRM. You can download the HWiNFO for free from the link given below.
Related:Best Free Hardware Monitoring & Information Utilities
Infrared Thermometer
The second easiest way to find out the VRM and Chipset temperature is by using an Infrared Thermometer or Infrared Temperature Gun. It is a small device that lets you find the temperature of any object without touching. Just hold it in your hand and direct it towards the object of which you want to find out the temperature, and then within a fraction of second, the temperature reading gets displayed on the LCD screen of the device. The device also comes with a built-in laser at its front end that lets you target and focus on smaller objects or at a particular point for better accuracy. So, if you want to find out about the temperature of your VRM or chipset, then open your computer case and point the laser of the temperature gun over the MOSFET / Chipset, or its heatsink to find out its temperature.
It must be noted that this device gives only the surface temperature of the object, so if your VRM or Chipset has heatsink over it then it will give you the temperature of the heatsink, which will be few degrees lower than the actual temperature of the component. An infrared thermometer is also very helpful to crosscheck the temperatures of the VRM and Chipset, even when the motherboard has sensors for them. This is because sometimes a bad sensor can report much lower or higher temperatures. So, it is a good practice to verify the temperatures with an infrared thermometer, even when everything is alright or when you have some doubts regarding their temperature. You can also find out your CPU heatsink temperature, graphics card VRM temperature, RAM temperature or temperature of other things using the infrared thermometer. These Infrared Thermometers can be found pretty cheap, and here are some affordable Infrared Thermometers that you can use for finding the temperature of any object including electronic components:
Etekcity Lasergrip 774 Infrared Thermometer
A cheap infrared thermometer that can be used to measure the temperature of any object including electronics and internal components of your computer. It can measure temperature in range of -58°F to 716°F / -50°C to +380°C with ±2% or 2°C. However, it has got fixed emissivity (0.95), which means you will have a hard time getting an accurate temperature reading from shiny surfaces or shiny metals that are bad at emitting their own infrared radiation, as they mostly emit ambient infrared radiation. But for the electronics, it will serve your purpose pretty good and can provide results with acceptable accuracy.
This IR Thermometer has 12:1 distance spot ratio and can measure the temperature of distant objects at pretty good accuracy. It comes with an LCD screen that is backlit, and for power, it requires a 9 Volt battery. The temperature response time is under 500ms, which is quite fast, and it can operate in the temperature range from 0°C to 50°C. The construction quality of the thermometer is good and it has got UV paint coating to resist scratches and wear. There is another model available Etekcity Lasergrip 1080 at a couple of dollars more that has higher temperature recording range of -58°F to 1022°F / -50°C to +550°C, while other features remain the same. You can check it out too from the links given below.
Note: To get the best accuracy, the distance between the thermometer and object of measurement should be around 14.17 inches (36cm).
| Etekcity Lasergrip 774 Infrared Thermometer Specifications | |
| Temperature Range | -58°F to 716°F / -50°C to +380°C |
| Accuracy | ±2% or 2°C |
| Emissivity | 0.95(fixed) |
| Laser Guidance | Single Laser |
| Battery | 9 Volt |
| Distance Spot Ratio | 12:1 |
| Features | Backlit LCD Screen, Auto-Off function, Low battery indicator, <500ms Response time |
Etekcity Lasergrip 1022 Infrared Thermometer
[Adjustable Emissivity, More Accurate]
This Infrared Thermometer comes with adjustable emissivity (0.1 – 1.0 Adjustable) to provide you better accuracy in measuring temperatures of shiny metals and other objects. It can measure temperature in the range of -58°F to 1022°F / -50°C to +550°C with an accuracy of ±2% or 2°F/2°C. For guidance and targeting, it comes with a single laser, and for display, it has got an LCD screen that is backlit. The distance spot ratio for this Infrared temperature gun is 12: 1 for measuring the temperature of far off objects with pretty good accuracy. The response time is under 500ms for super-fast measurement. It is solidly built has got UV coating over it for protection. A dual laser variant of this model is also available as Etekcity Lasergrip 1022D for better aiming, and you can check it out too from the links given below.
Note: For best accuracy, the distance between the thermometer and object of measurement should be kept at approximately 14.17 inches (36cm). I personally use Fluke IR Thermometer because it is a well-reputed brand and offers great quality and performance, but on the flip side, it costs a little extra.
| Etekcity Lasergrip 1022 Infrared Thermometer Specifications | |
| Temperature Range | -58°F to 1022°F / -50°C to +550°C |
| Accuracy | ±2% or 2°F/2°C |
| Emissivity | 0.1 – 1.0 Adjustable |
| Laser Guidance | Single Laser |
| Battery | 9 Volt |
| Distance Spot Ratio | 12:1 |
| Features | Backlit LCD Screen, Auto-Off function, Low battery indicator, <500ms Response time |
Thermal Probe / Temperature Sensor
Another great way to find out about your VRM and Chipset temperature is by using a Thermal Probe or Temperature sensor. These thermal sensors are based on the thermistor and come with a 2-pin connector that can be connected to the motherboard temperature sensor header (if you have any), supported aftermarket fan controller or standalone digital temperature displays that you can easily find in the market or online.
You can attach the thermal probe to the VRM, Chipset or any other component using thermal tape and then monitor the temperature using the temperature monitoring software such as HWiNFO or on the display of your fan controller or other digital temperature monitoring device with LCD display. These thermal probes can monitor the temperature to up to 125°C, which I think is sufficient enough. Below are some good thermal probes or temperature sensors that you can get for temperature monitoring of your internal PC components.
XSPC Wire Sensor 10K
[50cm Sleeved cable, 2-pin]
Phobya 10K Temperature Sensor

[80cm Sleeved cable, 2-pin]
Multimeter
You can also use a multimeter with temperature detection capability to measure the temperature of various objects including VRM and Chipset. This kind of multimeter comes with a thermal probe that you attach to the surface of the component using thermal tape and monitor its temperature. Besides measuring temperature, a multimeter is a very useful device that is used to measure voltage, resistance, current, frequency, continuity and for checking electronic components like a transistor, diode, capacitors, etc. It is also the best device for troubleshooting electronic and electrical components or devices. I personally think it is a must-have device if you are an enthusiast or work with computers and electronics. Here are some good multimeters that you can get for your troubleshooting needs.
AstroAI Digital Multimeter, TRMS 6000 Counts Multimeter
An Affordable Digital Multimeter that measures Voltage, Current, Resistance, Continuity, Capacitance, Frequency; Tests Diodes, Transistors, Temperature and more. It comes with a large LCD that is backlit and uses one 9V battery. Ideal for both household and commercial use.
Tacklife DM01M Advanced Digital Multimeter TRMS 6000 Counts
Another good budget digital multimeter that can measure temperature, and is great for both household and commercial applications. This multimeter uses four AA batteries for its working.
Msi Motherboard Temperature Monitor
Infrared Thermal Camera
A thermal camera not only measures temperature, but it can show all the heat zones of the object and its surroundings so that you can get a complete picture of what is going on. Just like Infrared Thermometer, a Thermal camera also uses infrared radiation to know about the temperature of the objects. However, it is a more complex and advanced device compared IR thermometer, and also way expensive than an IR thermometer. The main advantage of a thermal camera is that it paints a clear picture of the heating object and its surroundings, which allows you to make better and informed decisions to solve the ongoing issue. It has various other applications too e.g. to detect gaps, leaks in buildings or houses or HVAC checks. It is also known as a thermal imager, an infrared camera or thermal imaging camera. Here is a good thermal camera at a reasonable price that you can get for various tasks.
HTI HT-18 Infrared Thermal Camera
A basic handheld infrared thermal camera with a 3.2' display, having a resolution of 220 x 160 pixels. It can detect the temperature in the range of -20°C to 300°C (-4°F to 572°F) with an accuracy of ±2.5°C or ±2.5%. The camera comes with adjustable emissivity (0.1 to 1.0) and has a fixed focus mode. It uses 3.7V Built-in Rechargeable Battery and a USB interface for connectivity. Also, a 3GB SD card comes included with the camera itself. It is pretty lightweight and is one of the most affordable thermal cameras around that also delivers good performance.
How much VRM & Chipset Temperature is Safe?
This is a question that has been asked many times by users, and I think there is no specific answer to it as every motherboard chipset and VRM has its own threshold temperature limit. However, in general practice, it is better to keep VRM below 100°C and motherboard chipset or PCH under 70°C to be on the safer side because above these temperatures they lose out on performance and efficiency.
Nice tool Raymond!
ReplyLeave a Reply
(*This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may receive a small commission if you choose to purchase through links I provide (at no extra cost to you). Thank you for supporting the work I put into this site!)
If your motherboard chipset and VRM gets very hot, then they can lead to instability and other issues with your PC. VRM or Voltage Regulator Module is responsible for providing power to your processor or CPU and RAM. It converts higher 12V or 5V voltages from the PSU to a much lower voltage (1.2V or so) that is required by the CPU or processor. VRM mainly consists of MOSFETs, Inductors or Chokes, Capacitors, and a Logic Unit which is an Integrated Circuit (IC) and is called the PWM controller. MOSFETs are the main element of a VRM, and they can get very hot during high CPU usage, and especially during overclocking. Almost all of the mid-range and high-end motherboards come with heatsinks over VRMs for overclocking, so as to prevent them from overheating and thus avoiding any kind of system instability and unexpected shutdown.
Modern-day motherboard chipsets consist of I/O channels and Interfaces that include SATA ports, USB ports, RAID support, some PCI-E lanes and maybe some other things depending on the chipset. Basically, a motherboard chipset allows I/O devices and components to communicate with the CPU. Intel calls their motherboard chipset as PCH (Platform Hub Controller), whereas AMD calls it FCH (Fusion Controller Hub) or just motherboard chipset only.
A low-end motherboard chipset may not get that hot, but a mid-range and high-end motherboard chipset can get very hot and they are generally equipped with bigger heatsinks. Motherboard chipsets generally remain within the safe temperature range, but if they cross the threshold temperature then you can face various issues regarding stability.
Monitoring and knowing about your VRM and Motherboard temperature is very important, when you are facing any kind of instability issues with your system because these components often get ignored most of the time. So, here I am going to list down various methods to find out your motherboard chipset and VRM temperature, so that can you can take appropriate measures to cool them down.
How to Check VRM & Chipset Temperature
Here are the various methods and techniques by which you can monitor your motherboard's chipset and VRM temperature. Most of these methods can also be used to measure graphics card VRM temperature, and the temperature of its, GPU & VRAM.
HWiNFO
The easiest way to find out VRM and chipset temperature is by using HWiNFO, which is a very good hardware information and monitoring tool or utility. It should be noted that this method only works if your motherboard has built-in sensors for VRM and Chipset temperature monitoring. To know about the temperature of your motherboard chipset and VRM, launch the HWiNFO program, and from Menu bar, go to Monitoring->Sensor status. A window will open, and here scroll down to your motherboard section. For example, the motherboard listed here is Gigabyte B250-D2V-CF. Below that, you will find temperature readings for System, PCH, CPU and VRM MOS. PCH is your motherboard chipset and VRM MOS is the temperature of the MOSFETs of VRM, which are the main components of VRM. You can download the HWiNFO for free from the link given below.
Related:Best Free Hardware Monitoring & Information Utilities
Infrared Thermometer
The second easiest way to find out the VRM and Chipset temperature is by using an Infrared Thermometer or Infrared Temperature Gun. It is a small device that lets you find the temperature of any object without touching. Just hold it in your hand and direct it towards the object of which you want to find out the temperature, and then within a fraction of second, the temperature reading gets displayed on the LCD screen of the device. The device also comes with a built-in laser at its front end that lets you target and focus on smaller objects or at a particular point for better accuracy. So, if you want to find out about the temperature of your VRM or chipset, then open your computer case and point the laser of the temperature gun over the MOSFET / Chipset, or its heatsink to find out its temperature.
It must be noted that this device gives only the surface temperature of the object, so if your VRM or Chipset has heatsink over it then it will give you the temperature of the heatsink, which will be few degrees lower than the actual temperature of the component. An infrared thermometer is also very helpful to crosscheck the temperatures of the VRM and Chipset, even when the motherboard has sensors for them. This is because sometimes a bad sensor can report much lower or higher temperatures. So, it is a good practice to verify the temperatures with an infrared thermometer, even when everything is alright or when you have some doubts regarding their temperature. You can also find out your CPU heatsink temperature, graphics card VRM temperature, RAM temperature or temperature of other things using the infrared thermometer. These Infrared Thermometers can be found pretty cheap, and here are some affordable Infrared Thermometers that you can use for finding the temperature of any object including electronic components:
Etekcity Lasergrip 774 Infrared Thermometer
A cheap infrared thermometer that can be used to measure the temperature of any object including electronics and internal components of your computer. It can measure temperature in range of -58°F to 716°F / -50°C to +380°C with ±2% or 2°C. However, it has got fixed emissivity (0.95), which means you will have a hard time getting an accurate temperature reading from shiny surfaces or shiny metals that are bad at emitting their own infrared radiation, as they mostly emit ambient infrared radiation. But for the electronics, it will serve your purpose pretty good and can provide results with acceptable accuracy.
This IR Thermometer has 12:1 distance spot ratio and can measure the temperature of distant objects at pretty good accuracy. It comes with an LCD screen that is backlit, and for power, it requires a 9 Volt battery. The temperature response time is under 500ms, which is quite fast, and it can operate in the temperature range from 0°C to 50°C. The construction quality of the thermometer is good and it has got UV paint coating to resist scratches and wear. There is another model available Etekcity Lasergrip 1080 at a couple of dollars more that has higher temperature recording range of -58°F to 1022°F / -50°C to +550°C, while other features remain the same. You can check it out too from the links given below.
Note: To get the best accuracy, the distance between the thermometer and object of measurement should be around 14.17 inches (36cm).
| Etekcity Lasergrip 774 Infrared Thermometer Specifications | |
| Temperature Range | -58°F to 716°F / -50°C to +380°C |
| Accuracy | ±2% or 2°C |
| Emissivity | 0.95(fixed) |
| Laser Guidance | Single Laser |
| Battery | 9 Volt |
| Distance Spot Ratio | 12:1 |
| Features | Backlit LCD Screen, Auto-Off function, Low battery indicator, <500ms Response time |
Etekcity Lasergrip 1022 Infrared Thermometer
[Adjustable Emissivity, More Accurate]
This Infrared Thermometer comes with adjustable emissivity (0.1 – 1.0 Adjustable) to provide you better accuracy in measuring temperatures of shiny metals and other objects. It can measure temperature in the range of -58°F to 1022°F / -50°C to +550°C with an accuracy of ±2% or 2°F/2°C. For guidance and targeting, it comes with a single laser, and for display, it has got an LCD screen that is backlit. The distance spot ratio for this Infrared temperature gun is 12: 1 for measuring the temperature of far off objects with pretty good accuracy. The response time is under 500ms for super-fast measurement. It is solidly built has got UV coating over it for protection. A dual laser variant of this model is also available as Etekcity Lasergrip 1022D for better aiming, and you can check it out too from the links given below.
Note: For best accuracy, the distance between the thermometer and object of measurement should be kept at approximately 14.17 inches (36cm). I personally use Fluke IR Thermometer because it is a well-reputed brand and offers great quality and performance, but on the flip side, it costs a little extra.
| Etekcity Lasergrip 1022 Infrared Thermometer Specifications | |
| Temperature Range | -58°F to 1022°F / -50°C to +550°C |
| Accuracy | ±2% or 2°F/2°C |
| Emissivity | 0.1 – 1.0 Adjustable |
| Laser Guidance | Single Laser |
| Battery | 9 Volt |
| Distance Spot Ratio | 12:1 |
| Features | Backlit LCD Screen, Auto-Off function, Low battery indicator, <500ms Response time |
Thermal Probe / Temperature Sensor
Another great way to find out about your VRM and Chipset temperature is by using a Thermal Probe or Temperature sensor. These thermal sensors are based on the thermistor and come with a 2-pin connector that can be connected to the motherboard temperature sensor header (if you have any), supported aftermarket fan controller or standalone digital temperature displays that you can easily find in the market or online.
You can attach the thermal probe to the VRM, Chipset or any other component using thermal tape and then monitor the temperature using the temperature monitoring software such as HWiNFO or on the display of your fan controller or other digital temperature monitoring device with LCD display. These thermal probes can monitor the temperature to up to 125°C, which I think is sufficient enough. Below are some good thermal probes or temperature sensors that you can get for temperature monitoring of your internal PC components.
XSPC Wire Sensor 10K
[50cm Sleeved cable, 2-pin]
Phobya 10K Temperature Sensor
[80cm Sleeved cable, 2-pin]
Multimeter
You can also use a multimeter with temperature detection capability to measure the temperature of various objects including VRM and Chipset. This kind of multimeter comes with a thermal probe that you attach to the surface of the component using thermal tape and monitor its temperature. Besides measuring temperature, a multimeter is a very useful device that is used to measure voltage, resistance, current, frequency, continuity and for checking electronic components like a transistor, diode, capacitors, etc. It is also the best device for troubleshooting electronic and electrical components or devices. I personally think it is a must-have device if you are an enthusiast or work with computers and electronics. Here are some good multimeters that you can get for your troubleshooting needs.
AstroAI Digital Multimeter, TRMS 6000 Counts Multimeter
An Affordable Digital Multimeter that measures Voltage, Current, Resistance, Continuity, Capacitance, Frequency; Tests Diodes, Transistors, Temperature and more. It comes with a large LCD that is backlit and uses one 9V battery. Ideal for both household and commercial use.
Tacklife DM01M Advanced Digital Multimeter TRMS 6000 Counts
Another good budget digital multimeter that can measure temperature, and is great for both household and commercial applications. This multimeter uses four AA batteries for its working.
Msi Motherboard Temperature Monitor
Infrared Thermal Camera
A thermal camera not only measures temperature, but it can show all the heat zones of the object and its surroundings so that you can get a complete picture of what is going on. Just like Infrared Thermometer, a Thermal camera also uses infrared radiation to know about the temperature of the objects. However, it is a more complex and advanced device compared IR thermometer, and also way expensive than an IR thermometer. The main advantage of a thermal camera is that it paints a clear picture of the heating object and its surroundings, which allows you to make better and informed decisions to solve the ongoing issue. It has various other applications too e.g. to detect gaps, leaks in buildings or houses or HVAC checks. It is also known as a thermal imager, an infrared camera or thermal imaging camera. Here is a good thermal camera at a reasonable price that you can get for various tasks.
HTI HT-18 Infrared Thermal Camera
A basic handheld infrared thermal camera with a 3.2' display, having a resolution of 220 x 160 pixels. It can detect the temperature in the range of -20°C to 300°C (-4°F to 572°F) with an accuracy of ±2.5°C or ±2.5%. The camera comes with adjustable emissivity (0.1 to 1.0) and has a fixed focus mode. It uses 3.7V Built-in Rechargeable Battery and a USB interface for connectivity. Also, a 3GB SD card comes included with the camera itself. It is pretty lightweight and is one of the most affordable thermal cameras around that also delivers good performance.
How much VRM & Chipset Temperature is Safe?
This is a question that has been asked many times by users, and I think there is no specific answer to it as every motherboard chipset and VRM has its own threshold temperature limit. However, in general practice, it is better to keep VRM below 100°C and motherboard chipset or PCH under 70°C to be on the safer side because above these temperatures they lose out on performance and efficiency.
VRM should be under 100°C
Chipset should be under 70°C to 75°C
*Above 100°C, efficiency and performance of components decrease drastically.
How to Reduce VRM & Motherboard Chipset Temperature
There are a couple of ways to reduce your motherboard VRM and chipset temperature. If your motherboard VRM / Chipset has heatsink installed over it then it might be possible that the contact between the heatsink and the VRM MOSFET / Chipset is weak, which is causing high temperature. So, to solve this issue you have to install better thermal pads with adequate thickness for proper contact and heat transfer. To maximize cooling, you can also install a small 40mm or 60mm on the heatsink of the chipset, and around the VRM for actively cooling them, and thus reducing temperatures to greater levels.
In cases, where your motherboard VRM chipset & VRM does not come with heatsink installed, then the best way to cool them is by installing an additional small case fan (40mm or 60mm) in your case that blows air over them.
Final Words
Well, I think I have summed up pretty well on how you can check and monitor your motherboard's Chipset and VRM temperature. It is always better to know about the temperatures of the internal components of your PC so that you can take appropriate actions in time before any mishap happens. I strongly suggest you regularly monitor the temperature of your components once in a month or so at moderate to full load, as to make sure that everything is working fine or not. If you have any questions or doubts regarding this topic then you can ask your queries by leaving a comment below.

